AI/Machine Learning with confidence in Drug Discovery
This project aims at developing computational methods, tools and AI models to aid the drug discovery process. We primarily focus on ligand-based methods such as structure-activity relationships (SAR or QSAR). A special emphasis is on achieving a valid measure of confidence in predictions, and we apply Conformal Prediction methodology to this end. In order to analyze large-scale data we make use of modern e-infrastructure such as high-performance computing clusters, cloud computing resources, containerized microservice environments such as Kubernetes, and data analytics platforms such as Apache Spark.
Conformal Prediction
Conformal Prediction (CP) provides a layer on top of existing machine learning methods and produces valid prediction regions for test objects. This contrasts to standard machine learning that delivers point estimates. In CP a prediction region contains the true value with probability equal to 1 − ϵ, where ϵ is the selected confidence level. Such a prediction region can be obtained under the assumption that the observed data is exchangeable. An important consequence is that the size of this region directly relates to the strangeness of the test example, and is an alternative to the concept of a model’s applicability domain.
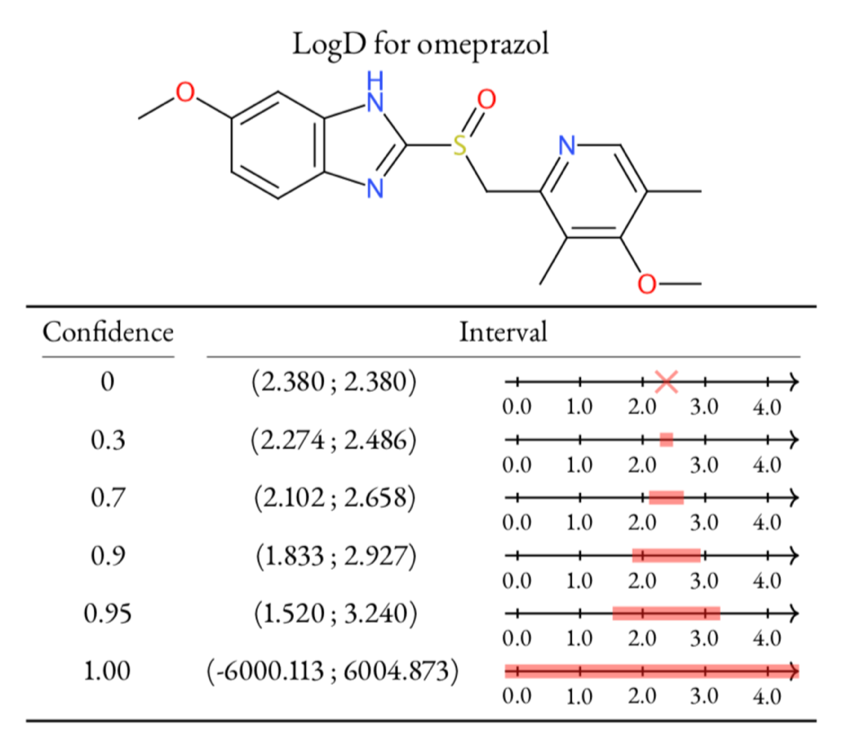
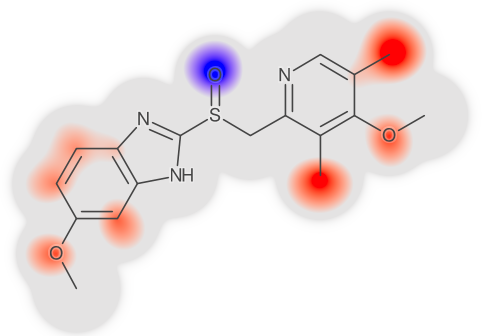
Left: Table of LogD prediction for omeprazol at different confidence levels using conformal prediction methodology. At confidence 0 the algorithm gives a single point and then as the confidence is increased, so is the interval. The only way to safely guarantee a correct prediction, i.e., confidence 1, is to provide an infinitely large interval. Right: Highlighting of atom contributions contributing to a prediction, where red color means contributing positively to the contribution, and blue negative contribution. Figure adapted from Alvarsson et al., J Pharm Sci 2020.
Large-scale AI modeling with workflows
Predictive modelling in drug discovery is challenging to automate as it often contains multiple analysis steps and might involve cross-validation and parameter tuning that create complex dependencies between tasks. With large-scale data or when using computationally demanding modelling methods, e-infrastructures such as high-performance or cloud computing are required, adding to the existing challenges of fault-tolerant automation. Workflow management systems can aid in many of these challenges.
We use and develop scientific workflow systems such as SciLuigi, SciPipe, and Pachyderm to automate and streamline analysis, especially for AI/ML in drug discovery. We also make use of modern e-infrastructure such as cloud computing, microservices, and containers.
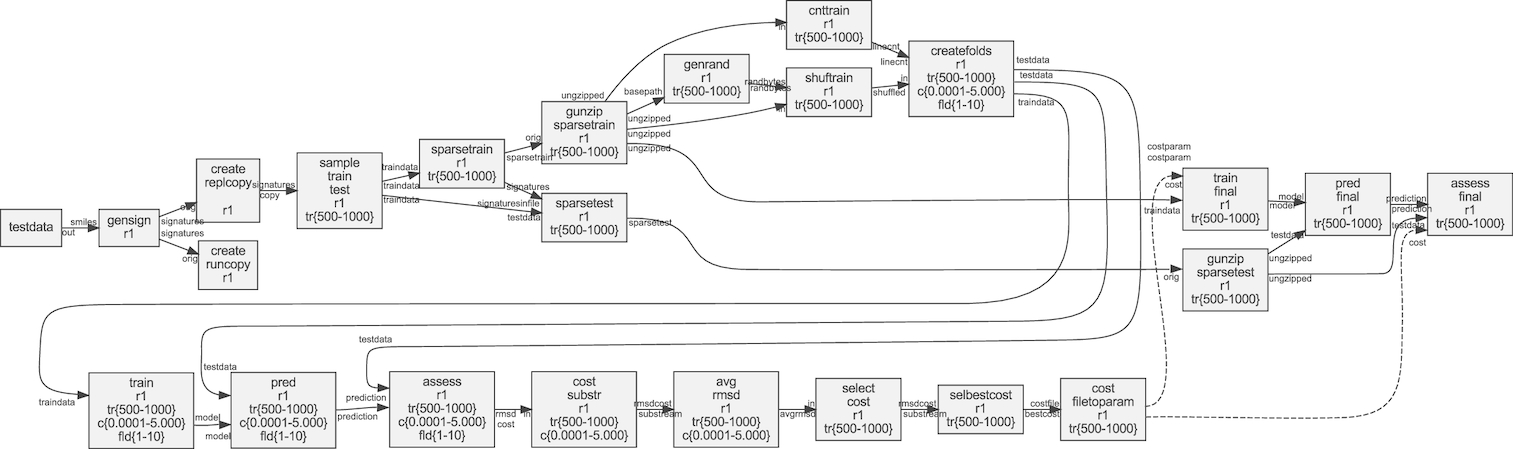 Figure: Example of a dynamic workflow for machine learning. Figure from Lampa et al., Gigascience. 8, 5 (2019)..
Figure: Example of a dynamic workflow for machine learning. Figure from Lampa et al., Gigascience. 8, 5 (2019)..
Site-of-metabolism prediction
This project aims at developing methods for predicting site-of-metabolism and metabolites based on chemical structure. Using data mining techniques we have developed the tools MetaPrint2D and MetPred for site-of-metabolism prediction. The project aims at improving these models and also to predict putative metabolites. The work is carried out in collaboration with AstraZeneca R&D.
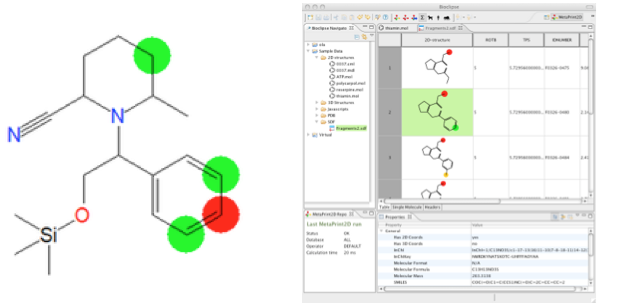
Figure: Prediction of site-of-metabolism with the MetaPrint2D method in Bioclipse.

